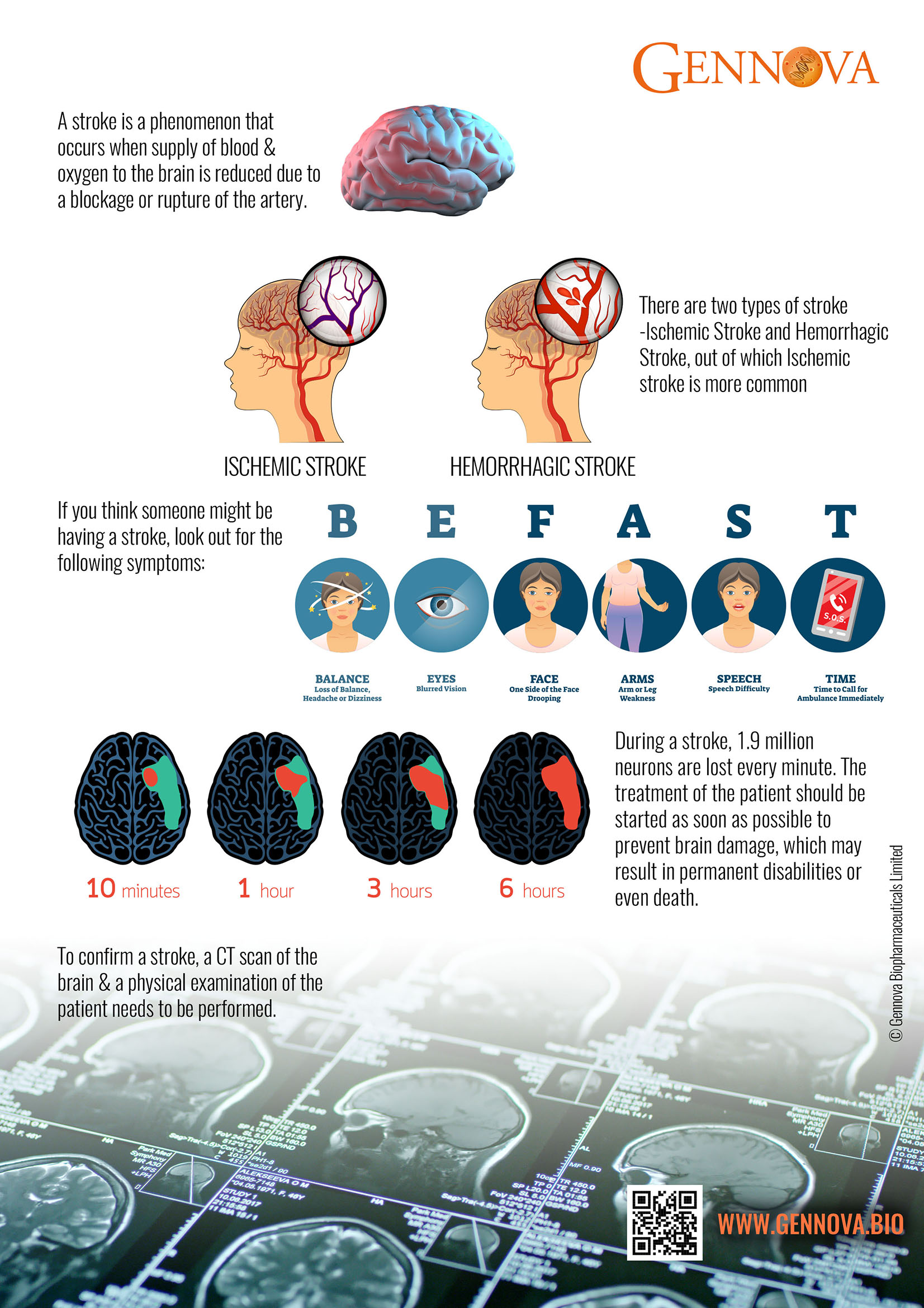
A stroke occurs when there’s bleeding or a blockage in the blood supply to the brain or heart that stops blood and oxygen supply.
There are two types of stroke: Hemorrhagic stroke (Only in brain) & Ischemic stroke (Brain & Heart). When an ischemic stroke affects the heart, it’s called as Ischemic Heart Disease (IHD) & when it affects the brain, it’s called Acute Ischemic Stroke (AIS).
The primary cause of an ischemic stroke is caused by a blockage in an artery that supplies blood to the brain, which may be a blood clot or a ruptured plaque, caused by atherosclerosis.’
How do we come to know if a person is suffering from a stroke? One or more of the following symptoms start appearing as soon as someone is having a stroke: paralysis, numbness/weakness in limbs (one side of the body), confusion, slurring speech, vision problems, in one or both eyes, trouble walking & maintaining balance & coordination, dizziness, severe & sudden headache.
Remembering all these at the time emergency may be difficult, therefore it is important to know to B E F A S T when someone around you might be having a stroke:
B alance
E ye trouble
F ace drooping
A rm weakness
S peech difficulty
T ime to call Medical help
What can be done in time of such an emergency? As soon as you notice the B E F A S T symptoms in the person, take the following measure while staying calm:
‐ Call emergency services.
‐ Make sure the patient is in a safe, comfortable position.
‐ Check the breathing, if the patient is not breathing, perform CPR.
‐ Put a blanket on them for warmth.
‐ Don’t give them anything to eat or drink.
‐ If the patient is showing any weakness in a limb, avoid moving them.
‐ Inform the emergency operator about the symptoms and how long ago they started.
‐ Mention if the person fell or hit their head.
It is very important to understand/realize the importance of time, when you are dealing with a stroke patient. When they say during a stroke, “Time is Brain” it is completely true as lack of blood supply to the brain kills 19 million neurons every minute. The delayed medical attention to a stroke patient results in irreparable brain damage or even death.
BURDEN OF STROKE
According to the statistical data provided by WHO, 15 million cases of stroke are reported every year out of which 5 million succumb to death & 5 million are permanently disabled. Stroke can happen to anyone. Around 60% of the patients are below the age of 70 & around 8% are below the age of 44. The death rate in younger population is 4%. In country like India, these percentages translate to a huge proportion of its population.
Earlier, until 2010, stroke incidences were more prevalent in developed nations. However, the recent statistics show that it has now become a disease of developing countries as well. The burden of stroke has been shifted from HICs to LMICs, and LMICs account for 85.5% of total stroke deaths worldwide. The number of disability-adjusted life years in LMICs was approximately seven times higher than that of high-income countries.
QUALITY OF LIFE
When a patient is dead or disabled, the family life is disturbed. Disabled patients become helpless & may suffer depression or other health complications, if not treated properly. Any type of disability burdens a family with financial challenges.
Stroke affects emotional quotient of the entire family of its victim. The mental trauma and emotional turbulence of the patient’s family are physically exhausting & can be devastating. Under such circumstances, family’s life & health become deteriorated, especially in the case of financially weak families. Disturbed emotional & financial conditions end up in strained social & personal relationships.

SOCIO-ECONOMIC BURDEN
In the society of a developing nation like India, when the younger population suffers from stroke, a void of prolific man force is created that leads to loss of productivity that leads to economic loss. A healthy & happy individual contributes to a healthy & happy society, and life after a stroke may take longer to come back to the normal, or to a new normal. This process can be mentally, physically & financially challenging. That is why we, as a society, should be putting efforts in preventing the stroke. For an ischemic stroke, social awareness is important, as the stroke is completely preventable & manageable.
How a stroke can be prevented? the simple answer to this question is by knowing the risk factors involved, and by avoiding them or controlling them. the two types of risk factors involved are: lifestyle-based, which include obesity, physical inactivity, heavy drinking & drug addiction. next category of risk factor consists of medical conditions like high blood pressure, smoking or exposure to smoke, high cholesterol, diabetes, obstructive sleep apnea, cardiovascular diseases, family history of stroke & COVID-19 infection, based on recent research.
PREPARATION & PREVENTION
To be aware and be prepared for a stroke is the key to minimizing the possibility of disabilities and leading a normal life. You can prepare for stroke by following steps:
– Educate your family and friends about “B E F A S T”
– Wear medical identification for medical staff
– Keep your updated medical history on hand
– Have the emergency contacts listed on your phone
– Keep a prescription of your medications with you
– Teach your children how to call for help
How can a stroke be prevented? To prevent the risk of stroke, we need to improve our lifestyle by changing habits that will put us in danger.
Few tips are as follows:
– Include more vegetables, beans & nuts in your daily diet
– Replace more seafood with red meat and poultry as much as possible
– Reduce intake of sodium, fats, sugars, and refined grains
– Cultivate habit of daily exercise
– Limit or, if possible, quit tobacco use
– Alcohol consumption should be moderate
– Take the prescribed medications for conditions, such as high blood pressure, as directed
A conclusive therapeutic approach, as soon as possible, aimed at removing the blockage by dissolving the clot (thrombolysis) or by removing it surgically (thrombectomy) can reduce the extent of brain damage. The core idea of survival is the rapid blood flow restoration.
The diagnostic tests that are performed to distinguish and confirm the type of stroke are: Physical Examination & CT and/or MRI scans.
As per the stroke management guidelines issued by the Govt of India, the blockage of a blood vessel should be cleared by an injection of ‘clot-buster drugs, also called as thrombolytes’ like Tenecteplase.