We often hear words like heart attack, paralysis and brain haemorrhage. These health conditions are collectively referred to as cardiovascular diseases (CVDs), which are the leading cause of death globally. CVD is a general term for conditions affecting the heart or blood vessels where the blood flow in the vessels is blocked.
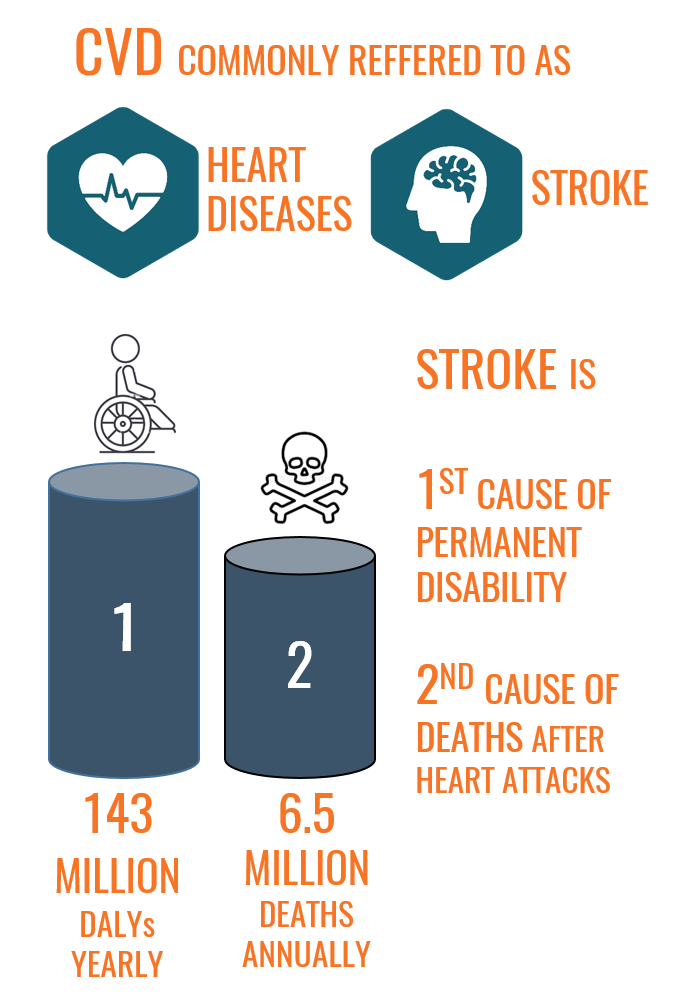
Stroke is a major contributor of CVDs, where the blood supply to a part of the brain is cut off. Stroke is the second-largest killer in the world after heart attacks and in 2020, 1 out of 6 deaths from CVDs was due to stroke (WHO).
Stroke causes more deaths annually, than those due to AIDS, tuberculosis and malaria combined. A stroke is also the leading cause of disability and causes wide-ranging short or long-term disabilities which require assistance.
The disability is expressed as DALYs (disability-adjusted life years) and one DALY is equivalent to loss of one healthy life year. Stroke is responsible for 143 million DALYs annually.
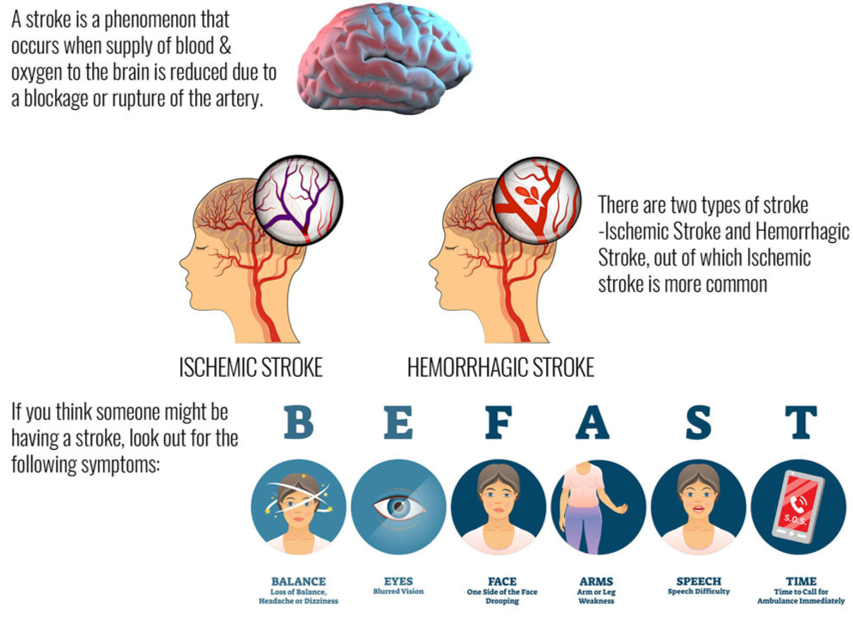
Stroke is of two types –
1.Ischemic stroke: occurs due to a blockage in the blood flow to the brain
2.Haemorrhagic stroke: caused by a damaged blood vessel preventing flow to the brain
Acute Ischemic Stroke (AIS) is the most common type, caused by the sudden loss/ reduction of blood supply to brain cells, depriving them of oxygen and nutrients. Without oxygen, brain cells begin to die, accompanied with a loss of function. During stroke, the patient feels weakness or numbness in one side of the body (paralysis) or a sudden headache or difficulty in speaking. The symptoms of a stroke can be remembered as ‘BE FAST’:
Balance; Eye trouble; Face drooping; Arm weakness; Speech difficulty; Time to call ambulance
A stroke not only affects the physical well-being but also the emotional status of the patient. Stroke can occur to anyone, anytime, anywhere and at any age. Stroke was earlier considered to be a disease of the developed nations and the aged. However, the increased incidence of stroke in the developing nations and in a younger population is alarming. The global burden of stroke is expected to rise further due to increasing population and aging. Stroke can be prevented by choosing a healthy lifestyle and controlling risk factors like blood pressure, diabetes, cholesterol etc

Stroke, is a condition of emergency and needs immediate attention and treatment. During a stroke, about 2 million brain cells (nerve cells or neurons) die with each passing minute. This may cause irreversible brain damage or even death. Thus, in order to minimize the damage, the blood flow to the affected brain area should be restored as soon as possible. This is done by removing the blockage (clot) in the blood vessel, either by breaking it (thrombolysis) or by removing it surgically (thrombectomy).
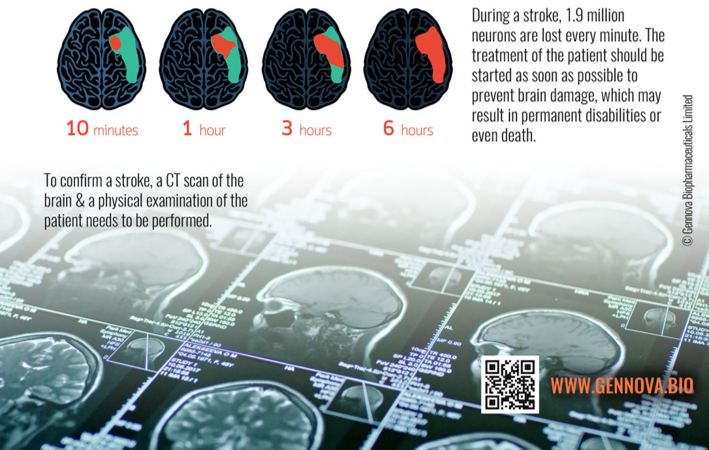
A clot is called as ‘thrombus’ which blocks the blood flow in the blood vessel and the process of breaking it, is called ‘thrombolysis’ (breaking up a thrombus). The medicines and drugs for bursting the clot are known as thrombolytics. These drugs act upon the constituents of a clot and break them free. This restores normal blood flow in the blocked blood vessel. These drugs are usually given within 4.5 hours from the start of the stroke symptoms.
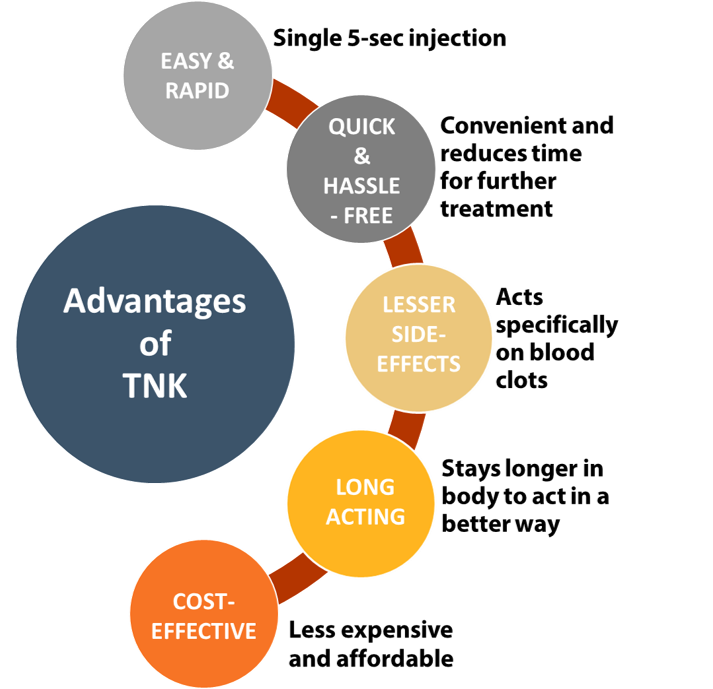
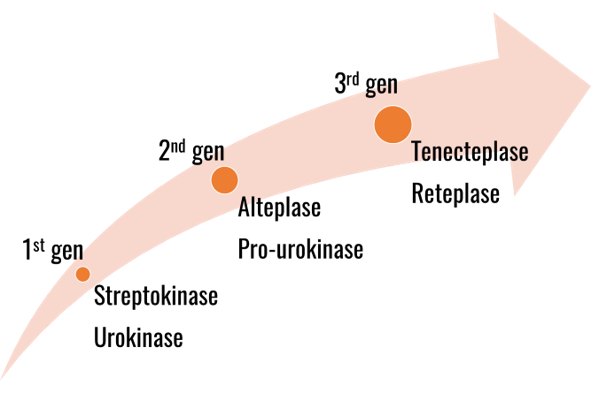
The thrombolytic drugs are classified into three generations based on their performance, such as streptokinase (1st gen), alteplase (2nd gen), tenecteplase and reteplase (3rd gen). The 1st and 2nd gen drugs are slow acting and are given as a slow drip (infusion in the blood) over a period of one hour. While, the 3rd gen thrombolytics can be given as a single injection. The new advanced drugs like tenecteplase (TNK) overcome most of the limitations of the earlier drugs and give it an edge as a time-saving, quick, easy and affordable treatment option.
- Easy and Rapid: Tenecteplase is a fast acting drug given as a single injection.
- Hassle-free: No IV pump or other equipment required and facilitates inter-hospital transfer of patients, if necessary.
- Long-Acting: Tenecteplase stays longer in blood and is 80-times more long lasting.
- Less adverse effects: Acts particularly on the blockages, thus has fewer adverse effects.
- Cost-effective: Tenecteplase offers a much cheaper and affordable treatment option as compared to currently used thrombolytic (alteplase).